Improve Efficiency for Walmart's Smart Logistics Warehouse System Using Python
In this project, I’m going to take the challenge of only using one package, Numpy, in Python that can efficiently provide Walmart’s 300 warehouses with product selection and how to replenish product supply on time in the event of a sudden out-of-stock situation.
Table of contents
- 00. Project Overview
- 01. Data Overview
- 02. Business Problem 1: Selecting The Best Product Mix For Each Warehouse
- 03. Solution For Business Problem 1
- 04. Business Problem 2: Top Alternative When A Random Warehouse Is Out-of-Stock
- 05. Solution for Business Problem 2
00. Project Overview
Context
Recently, Walmart is planning a 21-day countdown promotion for Christmas, and Marlon Brown, a manager of Walmart Company, must make sure that the stored products in each warehouse are proper and sufficient. After consideration, Marlon breaks this project into 2 parts:
1.Selecting products for each warehouse before the promotion starts
2.Simulating cross-warehouse-transshipment solution for possible product shortage problem for a random warehouse after the promotion starts
( Note: Can not use packages other than Numpy.)
Working as a consultant, I need to assist Marlon with my analysis to better preparation for the upcoming promotion.
Actions
For problem 1, I first needed to calculate the maximized total value and accumulated weight for one warehouse. I then applied it to the other left, creating a function “get_max_value” to help calculate the Value_Weight Ratio for each product, sort the Ratios in descending order, and select the products from the top of the descending order to the bottom while looking at the accumulated weight of products to make sure the accumulated weight does not exceed the warehouse weight capacity. And I got the optimal options, all the pairs of weights and values, by iterating through 300 warehouses.
For problem 2, Based on the selected warehouse p, I found the corresponding distance between this warehouse No.p and each of the other ones from the distance matrix. Then I calculated the “Value_per_Weight” ratio for each remaining warehouse taking distance and transpotation cost into consideration, sort the ratio in descending order and choose top helpers with 10 highest ratios.
Results
Preparing for the Christmas promotion, I suggested to the manager the best product selection for each warehouse, and if any one warehouse was out of stock, automatically generated the best inter-warehouse shipping plan.
Growth/Next Steps
Although the two problems of the manager are effectively solved through the program, they are all in a simulated environment after all. In the actual Walmart promotion event, the product and warehouse information will not be as simple as weight and value, there will be more variables and contingencies need to be considered, so more complex models may need to be introduced depending on the complexity of the business.
01. Data Overview
In the provided dataset named “Product.csv” as shown below, each column contains the weight and value of each product, and there are totally 50 available product options (Product No.0 - Product No.49) that can be selected into one warehouse.
Every two rows contain all product information in one warehouse, and there are 300 warehouses (Warehouse No.0 - Warehouse No.299) in total.
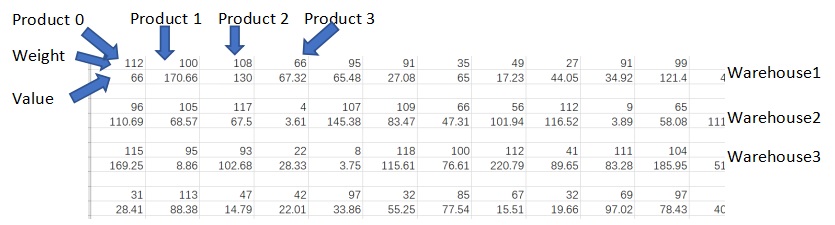
For each warehouse, there are 4 variables:
1.n - total number of products chosen to be stored in the warehouse
2.C - total weight capacity of the warehouse
3.Vi - the value of available product i
4.Wi - the weight of available product i
Specifically, for each warehouse, there is a weight capacity (C) of 650, which means that the total weight of n products that are selected to be stored in a warehouse should be less than or equal to 650. Each available product i has its own weight (Wi) and value (Vi). Besides, the product information for each warehouse is different.
02. Business Problem 1: Selecting The Best Product Mix For Each Warehouse
The manager wants to choose products that have the top “Value_Weight Ratios” as many as possible before reaching the capacity of each warehouse (650).
Calculating the estimated total value and accumulated weight of each 300 warehouses will be helpful for the later decision of cross-warehouse-transshipment solution.
03. Solution for Business Problem 1
I utlise the numpy package within Python to optimize the product selection. The code sections below are broken up into 4 key sections:
- Data Import
- Estimating Value And Weight For One Warehouse
- Model Training
- Performance Assessment
Data Import
Since we saved our modelling data as a pickle file, we import it. We ensure we remove the id column, and we also ensure our data is shuffled.
# Numpy package is the only package I could use for this project
import numpy as np
# Read the dataset from "Products.csv"
# Using .open() method to open files and return a file object
file_name='Products.csv'
f = open(file_name, "r")
Estimating Value And Weight For One Warehouse
let’s write a function “get_max_value” which could do the following 4 things:
- Calculate the Value_Weight Ratio for each product.
- Sort the calculated Value_Weight Ratios in descending order.
- Select the products from the top of the descending order to the bottom while looking at the accumulated weight of products to make sure the accumulated weight does not exceed the warehouse weight capacity.
- Calculate the corresponding total value and accumulated weight for this warehouse after finishing product selection.
def get_max_value(weights, values):
# convert String to float and compute ratio
weightNumber = []
valueNumber = []
for i in range(len(weights)):
x = float(weights[i])
y = float(values[i])
weightNumber.append(x)
valueNumber.append(y)
Array1=np.array(weightNumber)
Array2=np.array(valueNumber)
#this is the ratio
ratio = Array2/Array1
# print(ratio)
map = {}
for i in range(len(ratio)):
map[i] = ratio[i]
# sort the map
marklist = sorted(map.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
# this is ratio and item index sorting descending order in ratio
sortdict = dict(marklist)
# print(sortdict)
capacity = 650
sumCapacity = 0
#interate from sorted dict and find out what items to be chosen based on capacity
maxValue = 0
weightToValue = {}
for key in sortdict:
if (sumCapacity + weightNumber[key] < capacity):
sumCapacity += weightNumber[key]
maxValue += valueNumber[key]
# print(sumCapacity) this is total capacity
weightToValue[sumCapacity] = maxValue
return weightToValue
Estimating the Total Value for 300 Warehouses
Let’s apply the same calculation process of previous step for one warehouse to the 299 warehouses left.
# we have 300 instances and one warehouse has 3 rows on the dataset. So, we will iterate for 900
storeValueCapacity = {}
for i in range(0,900,3):
lineWeight = f.readline().replace(' ', '').split(",")
lineValue = f.readline().replace(' ', '').split(",")
f.readline()
storeValueCapacity[i / 3] = get_max_value(lineWeight, lineValue)
print(storeValueCapacity)
04. Business Problem 2: Top Alternative When A Random Warehouse Is Out-of-Stock
Generating the 300 X 300 distance matrix
Each of the distances can be generated by using a normal distribution with a mean of 500 and a standard deviation of 300.
All the distances generated should be positive numbers and should be rounded to integers using the round() function. After successfully generating the distance matrix, please write it to a new CSV file called “Distances.csv”.
05. Solution for Business Problem 2
# Generate the Distance matrix 300*300
distances = np.random.normal(500, 300, size=(300, 300))
# Check the maxtrix and see if all numbers are positive and rounded to integer
for i in range(300):
for j in range(len(distances[i])):
distances[i][j] = abs(distances[i][j]).round()
distances
# save the file in 'Distance.csv'
f = open("Distances.csv", "w")
# write a row to the csv file
for i in range(len(distances)):
f.write(', '.join(str(distance) for distance in distances[i])+'\n')
# close the file
f.close()
Selecting the Alternative Warehouse (“Helper”)
The manager randomly selects No.p warehouse that is out-of-stock in this simulation.
There are 3 things to do:
- Based on the generated p, find the corresponding distance between this warehouse No.p and each of the other Helpers from the distance matrix generated in the previous step.
- Find the corresponding total value and total weight of all products stored in each Helper (have calculated these numbers in Problem 1).
- Calculate the “Value_per_Weight” ratio for each Helper (formula as below), sort the ratio in descending order and choose top helpers with 10 highest “Value_per_Weight”ratios.
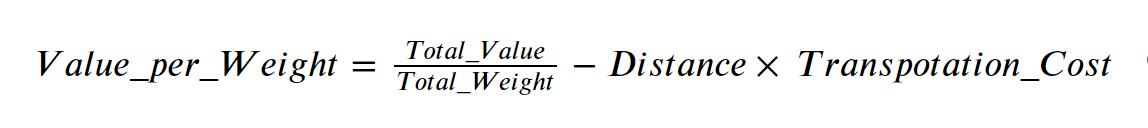
( The solution should contain Helper indexes and the corresponding “Value_Per_Weight” ratios. )
# p is offered by the manager.
p=np.random.randint(0,300)
p
# Show the cross-warehouse-transshipment solution when No.p warehouse is out-of-stock during the promotion period.
distance = distances[p]
# print(storeValueCapacity)
storeValuePerWeight = {}
for i in range(300):
for key in storeValueCapacity[i]:
valuePerWeight = storeValueCapacity[i][key] / key - distance[i] * 0.015
storeValuePerWeight[i] = valuePerWeight
list = sorted(storeValuePerWeight.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
#this is ratio and item index sorting descending order in ratio
sortedStoreValuePerWeight = dict(list)
print(sortedStoreValuePerWeight)
print("\n")
list_10=list[0:10]
dict_10=dict(list_10)
print(dict_10)
# Note: Due to random assignment of No.p warehouse, it's acceptable if the recommended solution changes each time you re-run the code.